7 Online LiDAR - Advanced Topics
7.1 Introduction
The RoboSense LiDAR may work
in unicast/multicast/broadcast mode,
with VLAN layer
with user layers.
Also rslidar_sdk supports multi-LiDARs.
This document illustrates how to configure rslidar_sdk in each case.
Before reading this document, please be sure that you have read:
LiDAR user-guide
7.2 Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast
7.2.1 Broadcast mode
The Lidar sends MSOP/DIFOP packets to the host machine (rslidar_sdk runs on it). For simplicity, the DIFOP port is ommited here.
The Lidar sends to
255.255.255.255:6699, and the host binds to port6699.
Below is how to configure config.yaml.
common:
msg_source: 1
send_point_cloud_ros: true
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
ros:
ros_frame_id: rslidar
ros_send_point_cloud_topic: /rslidar_points
The common part and the lidar-ros part is listed here. They will be ommited in the following examples, since they are not changed.
7.2.2 Unicast mode
To reduce the network load, the Lidar is suggested to work in unicast mode.
The Lidar sends to
192.168.1.102:6699, and the host binds to port6699.
Below is how to configure config.yaml. In fact, it same with the broadcast mode.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
7.2.3 Multicast mode
The Lidar may also works in multicast mode.
The lidar sends to
224.1.1.1:6699The host binds to port
6699. And it makes local NIC (Network Interface Card) join the multicast group224.1.1.1. The local NIC’s IP is192.168.1.102.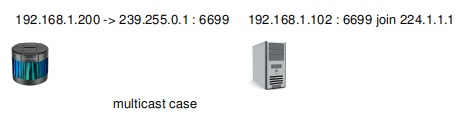
Below is how to configure config.yaml.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
group_address: 224.1.1.1
host_address: 192.168.1.102
7.3 Multiple LiDARs
7.3.1 Different remote ports
If you have two or more Lidars, it is suggested to set different remote ports.
First Lidar sends to
192.168.1.102:6699, and the first driver instance binds to6699.Second Lidar sends to
192.168.1.102:5599, and the second driver instance binds to5599.
Below is how to configure config.yaml.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 5599
difop_port: 6688
7.3.2 Different remote IPs
An alternate way is to set different remote IPs.
The host has two NICs:
192.168.1.102and192.168.1.103.First Lidar sends to
192.168.1.102:6699, and the first driver instance binds to192.168.1.102:6699.Second Lidar sends to
192.168.1.103:6699, and the second driver instance binds to192.168.1.103:6699.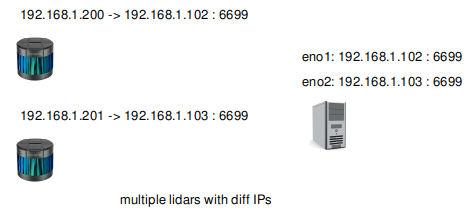
Below is how to configure config.yaml.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
host_address: 192.168.1.102
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
host_address: 192.168.1.103
7.4 VLAN
In some user cases, The Lidar may work on VLAN. Its packets have a VLAN layer.
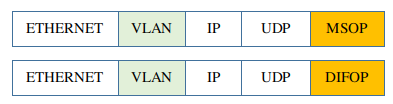
The driver cannot parse this packet. Instead, it depends on a virtual NIC to strip the VLAN layer.
Below is an example.
The Lidar works on VLAN
80. It sends packets to192.168.1.102:6699. The packet has a VLAN layer.Suppose there is a physical NIC
eno1on the host. It receives packets with VLAN layer.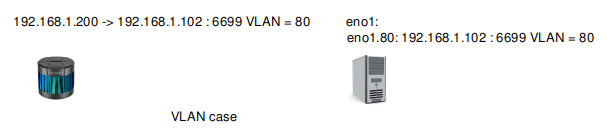
To strip the VLAN layer, create a virtual NIC eno1.80 on eno1, and assign IP 192.168.1.102 to it.
sudo apt-get install vlan -y
sudo modprobe 8021q
sudo vconfig add eno1 80
sudo ifconfig eno1.80 192.168.1.102 up
Now the driver may take eno1.80 as a general NIC, and receives packets without VLAN layer.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
7.5 User Layer, Tail Layer
In some user cases, User may add extra layers before or after the MSOP/DIFOP packet.
USER_LAYER is before the packet and TAIL_LAYER is after it.
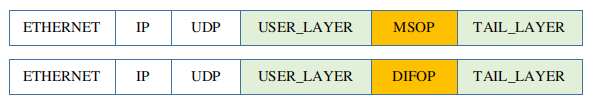
These extra layers are parts of UDP data. The driver can strip them.
To strip them, just give their lengths in bytes.
In the following example, USER_LAYER is 8 bytes, and TAIL_LAYER is 4 bytes.
lidar:
- driver:
lidar_type: RS32
msop_port: 6699
difop_port: 7788
user_layer_bytes: 8
tail_layer_bytes: 4