Benchmarking¶
Note
To use this benchmarking method, you will need to download and install the ROS Warehouse plugin. Currently this is not available from Debians and requires a source install for at least some aspects. For source instructions, see this page
Getting Started¶
If you haven’t already done so, make sure you’ve completed the steps in Getting Started.
The benchmarking package provides methods to benchmark motion planning algorithms and aggregate/plot statistics using the OMPL Planner Arena. The example below demonstrates how the benchmarking can be run for a Panda robot arm.
Example¶
An example is provided in the examples folder. The launch file requires a MoveIt configuration package
for the Panda robot arm available from here.
To run:
Launch the panda_moveit_config
demo.launch:roslaunch panda_moveit_config demo.launch db:=true
Within the Motion Planning RViz plugin, connect to the database by pressing the Connect button in the Context tab.
Save a scene on the Stored Scenes tab and name it
Kitchen1by double clicking the scene in the list.Move the start and goal states of the Panda arm by using the interactive markers.
Save an associated query for the
Kitchen1scene and name the queryPick1.Also save a start state for the robot on the Stored States tab and name it
Start1.The config file
moveit_ros/benchmarks/examples/demo1.yamlrefers to the scenes, queries and start states used for benchmarking. Modify them appropriately.Bring down your previous launch file (
ctrl+c).Change the location
output_directoryto export the benchmarked files:rosed moveit_ros_benchmarks demo1.yaml
Run the benchmarks:
roslaunch moveit_ros_benchmarks demo_panda.launch
Viewing Results¶
The benchmarks are executed and many interesting parameters are aggregated and written to a log file. A script (moveit_benchmark_statistics.py) is supplied to parse this data and plot the statistics.
Run:
rosrun moveit_ros_benchmarks moveit_benchmark_statistics.py <path_of_logfile>
To generate a PDF of plots:
python -p <plot_filename> moveit_benchmark_statistics.py <path_of_logfile>
Alternatively, upload the database file generated by moveit_benchmark_statistics.py to plannerarena.org and interactively visualize the results.
Parameters of the BenchmarkOptions Class¶
This class reads in parameters and options for the benchmarks to run from the ROS parameter server. The format of the parameters is assumed to be in the following form:
benchmark_config:
warehouse:
host: [hostname/IP address of ROS Warehouse node] # Default localhost
port: [port number of ROS Warehouse node] # Default 33829
scene_name: [Name of the planning scene to use for benchmarks] # REQUIRED
parameters:
runs: [Number of runs for each planning algorithm on each request] # Default 10
group: [The name of the group to plan] # REQUIRED
timeout: [The maximum time for a single run; seconds] # Default 10.0
output_directory: [The directory to write the output to] # Default is current working directory
start_states: [Regex for the stored start states in the warehouse to try] # Default ""
path_constraints: [Regex for the path constraints to benchmark] # Default ""
queries: [Regex for the motion plan queries in the warehouse to try] # Default .*
goal_constraints: [Regex for the goal constraints to benchmark] # Default ""
trajectory_constraints: [Regex for the trajectory constraints to benchmark] # Default ""
workspace: [Bounds of the workspace the robot plans in. This is an AABB] # Optional
frame_id: [The frame the workspace parameters are specified in]
min_corner: [Coordinates of the minimum corner of the AABB]
x: [x-value]
y: [y-value]
z: [z-value]
max_corner: [Coordinates of the maximum corner of the AABB]
x: [x-value]
y: [y-value]
z: [z-value]
planners:
- plugin: [The name of the planning plugin the planners are in] # REQUIRED
planners: # REQUIRED
- A list of planners
- from the plugin above
- to benchmark the
- queries in.
- plugin: ...
- ...
Parameters of the BenchmarkExecutor Class¶
This class creates a set of MotionPlanRequests that respect the parameters given in the supplied instance of BenchmarkOptions and then executes the requests on each of the planners specified. From the BenchmarkOptions, queries, goal_constraints, and trajectory_constraints are treated as separate queries. If a set of start_states is specified, each query, goal_constraint, and trajectory_constraint is attempted with each start state (existing start states from a query are ignored). Similarly, the (optional) set of path constraints is combined combinatorially with the start query and start goal_constraint pairs (existing path_constraint from a query are ignored). The workspace, if specified, overrides any existing workspace parameters.
The benchmarking pipeline does not utilize MoveGroup, and PlanningRequestAdaptors are not invoked.
It is possible to customize a benchmark run by deriving a class from BenchmarkExecutor and overriding one or more of the virtual functions. Additionally, a set of functions exists for ease of customization in derived classes:
preRunEvent: invoked immediately before each call to solvepostRunEvent: invoked immediately after each call to solveplannerSwitchEvent: invoked when the planner changes during benchmarkingquerySwitchEvent: invoked before a new benchmark problem begin execution
Note, in the above, a benchmark is a concrete instance of a PlanningScene, start state, goal constraints / trajectory_constraints, and (optionally) path_constraints. A run is one attempt by a specific planner to solve the benchmark.
Benchmarking of Different Motion Planners: CHOMP, STOMP and OMPL¶
This section contains the instructions for benchmarking different motion planners present in MoveIt: CHOMP, STOMP and OMPL. These planners can be compared with each other for a well defined benchmark (which is for the same environment, start states, queries and goal states). Different metrics for each of the planners can be reported to get quantitative statistics which could aid in proper selection of a particular planner in a defined environment. The statistics reported for each of the planners includes: time taken to compute the path, path length, path time, whether a valid path was found or not, etc.
Benchmarking in a scene without obstacles¶
To benchmark different planners in a simple environment without obstacles, open one terminal and follow the steps in the Example section at the top of this page. In the last two steps instead of editing demo1.yaml and launching demo_panda.launch, edit demo_panda_all_planners.yaml and launch demo_panda_all_planners.launch.
Benchmarking in a scene with obstacles¶
To benchmark motion planners in a scene filled with obstacles, open two terminals. In the first terminal start RViz and wait for everything to finish loading:
roslaunch panda_moveit_config demo.launch db:=true
In the second terminal, run either of the two commands:
rosrun moveit_tutorials collision_scene_example.py sparse
or:
rosrun moveit_tutorials collision_scene_example.py cluttered
Now follow these steps:
Within the Motion Planning RViz plugin, connect to the database by pressing the Connect button in the Context tab.
Save a scene on the Stored Scenes tab and name it
ObstaclesSceneby double clicking the scene in the list.Move the start and goal states of the Panda arm by using the interactive markers.
Save an associated query for the
ObstaclesScenescene and name the queryPick1.Also save a start state for the robot on the Stored States tab and name it
Start1.The config file
moveit_ros/benchmarks/examples/demo_obstacles.yamlrefers to the scenes, queries and start states used for benchmarking. Modify them appropriately.Bring down your previous launch file (
ctrl+c).Change the location
output_directoryto export the benchmarked files:rosed moveit_ros_benchmarks demo_obstacles.yaml
Run the benchmarks:
roslaunch moveit_ros_benchmarks demo_panda_all_planners_obstacles.launch
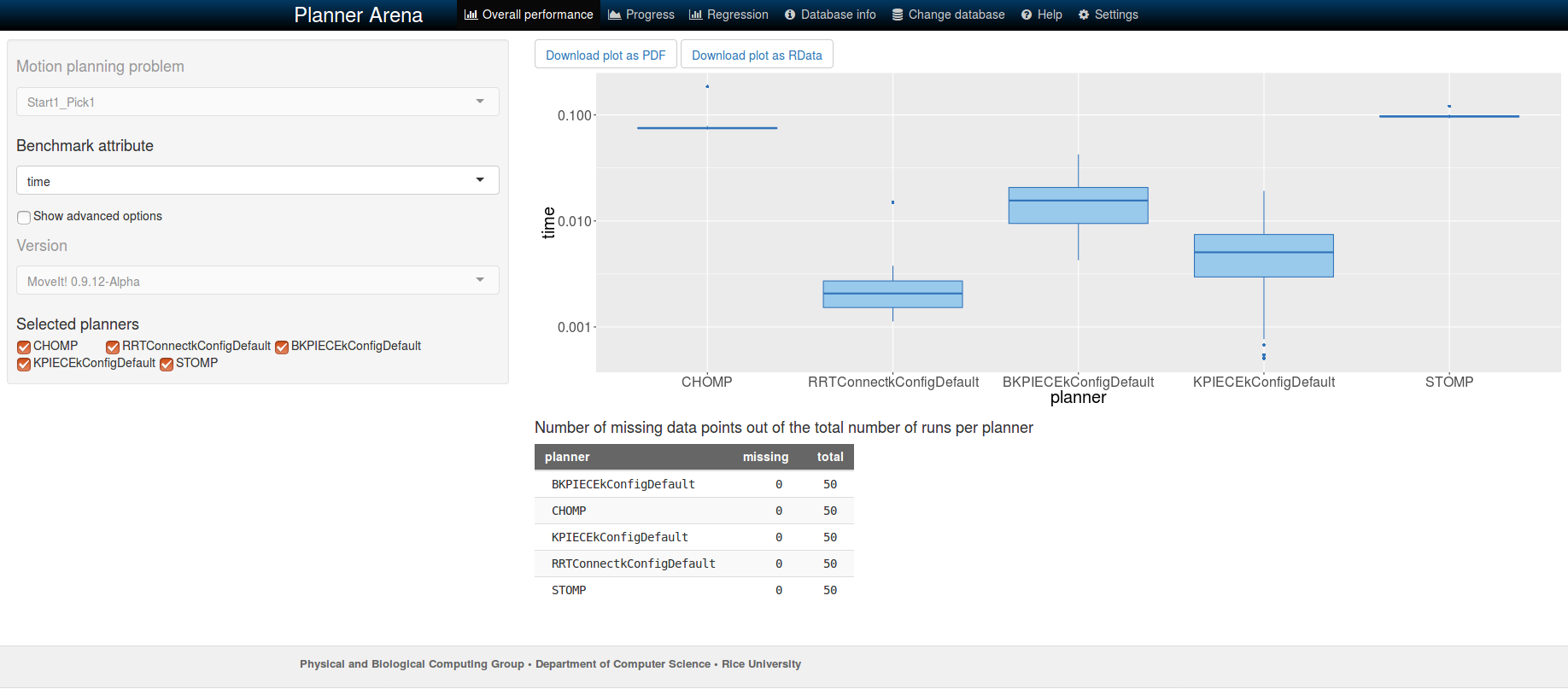
To view the results follow the same steps as listed in the Viewing Results section above. After loading the database into Planner arena, different statistics can be analysed about each of the planners by choosing the required benchmark attribute from the drop down list (see figure). See image below for analysis of time taken by each of the planners to compute the solution for a sample benchmark.
Open Source Feedback
See something that needs improvement? Please open a pull request on this GitHub page