Vectorized image operations. More...
#include "generic.h"

Go to the source code of this file.
Defines | |
Image convolution flags | |
| #define | VL_PAD_BY_ZERO (0x0 << 0) |
| Pad with zeroes. | |
| #define | VL_PAD_BY_CONTINUITY (0x1 << 0) |
| Pad by continuity. | |
| #define | VL_PAD_MASK (0x3) |
| Padding field selector. | |
| #define | VL_TRANSPOSE (0x1 << 2) |
| Transpose result. | |
Functions | |
Image convolution | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imconvcol_vf (float *dst, vl_size dst_stride, float const *src, vl_size src_width, vl_size src_height, vl_size src_stride, float const *filt, vl_index filt_begin, vl_index filt_end, int step, unsigned int flags) |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imconvcol_vd (double *dst, vl_size dst_stride, double const *src, vl_size src_width, vl_size src_height, vl_size src_stride, double const *filt, vl_index filt_begin, vl_index filt_end, int step, unsigned int flags) |
| Convolve image along columns. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imconvcoltri_f (float *dest, vl_size destStride, float const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride, vl_size filterSize, vl_size step, int unsigned flags) |
| Convolve an image along the columns with a triangular kernel. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imconvcoltri_d (double *dest, vl_size destStride, double const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride, vl_size filterSize, vl_size step, int unsigned flags) |
| Convolve an image along the columns with a triangular kernel. | |
Integral image | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imintegral_f (float *integral, vl_size integralStride, float const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| Compute integral image. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imintegral_d (double *integral, vl_size integralStride, double const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| Compute integral image. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imintegral_i32 (vl_int32 *integral, vl_size integralStride, vl_int32 const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| Compute integral image. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imintegral_ui32 (vl_uint32 *integral, vl_size integralStride, vl_uint32 const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| Compute integral image. | |
Distance transform | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_image_distance_transform_d (double const *image, vl_size numColumns, vl_size numRows, vl_size columnStride, vl_size rowStride, double *distanceTransform, vl_uindex *indexes, double coeff, double offset) |
| Compute the distance transform of an image. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_image_distance_transform_f (float const *image, vl_size numColumns, vl_size numRows, vl_size columnStride, vl_size rowStride, float *distanceTransform, vl_uindex *indexes, float coeff, float offset) |
Image smoothing | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imsmooth_f (float *smoothed, vl_size smoothedStride, float const *image, vl_size width, vl_size height, vl_size stride, double sigmax, double sigmay) |
| Smooth an image with a Gaussian filter. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imsmooth_d (double *smoothed, vl_size smoothedStride, double const *image, vl_size width, vl_size height, vl_size stride, double sigmax, double sigmay) |
| Smooth an image with a Gaussian filter. | |
Image gradients | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imgradient_polar_f (float *amplitudeGradient, float *angleGradient, vl_size gradWidthStride, vl_size gradHeightStride, float const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imgradient_polar_d (double *amplitudeGradient, double *angleGradient, vl_size gradWidthStride, vl_size gradHeightStride, double const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| Compute gradient mangitudes and directions of an image. | |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imgradient_f (float *xGradient, float *yGradient, vl_size gradWidthStride, vl_size gradHeightStride, float const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imgradient_d (double *xGradient, double *yGradient, vl_size gradWidthStride, vl_size gradHeightStride, double const *image, vl_size imageWidth, vl_size imageHeight, vl_size imageStride) |
| VL_EXPORT void | vl_imgradient_polar_f_callback (float const *sourceImage, int sourceImageWidth, int sourceImageHeight, float *dstImage, int dstWidth, int dstHeight, int octave, int level, void *params) |
Detailed Description
Vectorized image operations.
This module provides the following image operations:
- Separable convolution. The function vl_imconvcol_vf() can be used to compute separable convolutions.
- Convolution by a triangular kernel. The function vl_imconvcoltri_vf() is an optimized convolution routine for triangular kernels.
- Distance transform. vl_image_distance_transform_f() is a linear algorithm to compute the distance transform of an image.
- Remarks:
- Some operations are optimized to exploit possible SIMD instructions. This requires image data to be properly aligned (typically to 16 bytes). Similalry, the image stride (the number of bytes to skip to move to the next image row), must be aligned.
Definition in file imopv.h.
Define Documentation
| #define VL_PAD_BY_CONTINUITY (0x1 << 0) |
| #define VL_PAD_BY_ZERO (0x0 << 0) |
| #define VL_PAD_MASK (0x3) |
| #define VL_TRANSPOSE (0x1 << 2) |
Function Documentation
| vl_image_distance_transform_d | ( | double const * | image, |
| vl_size | numColumns, | ||
| vl_size | numRows, | ||
| vl_size | columnStride, | ||
| vl_size | rowStride, | ||
| double * | distanceTransform, | ||
| vl_uindex * | indexes, | ||
| double | coeff, | ||
| double | offset | ||
| ) |
Compute the distance transform of an image.
- Parameters:
-
image image. numColumns number of columns of the image. numRows number of rows of the image. columnStride offset from one column to the next. rowStride offset from one row to the next. distanceTransform distance transform (out). indexes nearest neighbor indexes (in/out). coeff quadratic cost coefficient (non-negative). offset quadratic cost offset.
The function computes the distance transform along the first dimension of the image image. Let  be image. Its distance transfrom
be image. Its distance transfrom  is given by:
is given by:
![\[ u^*(u,v) = \min_{u'} I(u',v) + \mathtt{coeff} (u' - u - \mathtt{offset})^2, \quad D(u,v) = I(u^*(u,v),v). \]](form_98.png)
Notice that coeff must be non negative.
The function fills in the buffer distanceTransform with  . This buffer must have the same size as image.
. This buffer must have the same size as image.
If indexes is not NULL, it must be a matrix of the same size o the image. The function interprets the value of this matrix as indexes of the pixels, i.e  is the index of pixel
is the index of pixel  . On output, the matrix indexes contains
. On output, the matrix indexes contains  . This information can be used to determine for each pixel
. This information can be used to determine for each pixel  its “nearest neighbor&rdquo.
its “nearest neighbor&rdquo.
Notice that by swapping numRows and numColumns and columnStride and rowStride, the function can be made to operate along the other image dimension. Specifically, to compute the distance transform along columns and rows, call the functinon twice:
for (i = 0 ; i < numColumns * numRows ; ++i) indexes[i] = i ; vl_image_distance_transform_d(image,numColumns,numRows,1,numColumns, distanceTransform,indexes,u_coeff,u_offset) ; vl_image_distance_transform_d(distanceTransform,numRows,numColumns,numColumns,1, distanceTransform,indexes,u_coeff,u_offset) ;
- Algorithm
The function implements the algorithm described in: P. F. Felzenszwalb and D. P. Huttenlocher, Distance Transforms of Sampled Functions, Technical Report, Cornell University, 2004.
Since the algorithm operates along one dimension per time, consider the 1D version of the problem for simplicity:
![\[ d(y) = \min_{x} g(y;x), \quad g(y;x) = f(x) + \alpha (y - x - \beta)^2, \quad x,y \in \{0,1,\dots,N-1\}. \]](form_103.png)
Hence the distance transform 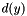 is the lower envelope of the family of parabolas
is the lower envelope of the family of parabolas  indexed by
indexed by 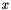 . Notice that all parabolas have the same curvature and that their centers are located at
. Notice that all parabolas have the same curvature and that their centers are located at 
 . The algorithm considers one parabola per time, from left to right, and finds the interval for which the parabola belongs to the lower envelope (if any).
. The algorithm considers one parabola per time, from left to right, and finds the interval for which the parabola belongs to the lower envelope (if any).
Initially, only the leftmost parabola 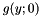 has been considered, and its validity interval is
has been considered, and its validity interval is 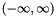 . Then the second parabola
. Then the second parabola 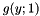 is considered. As long as
is considered. As long as  , the two parabolas
, the two parabolas 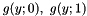 intersect at a unique point
intersect at a unique point 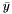 . Then the first parabola belongs to the envelope in the interval
. Then the first parabola belongs to the envelope in the interval ![$ (-\infty, \bar y] $](form_115.png) and the second one in the interval
and the second one in the interval ![$ (\bar y, +\infty] $](form_116.png) . When the third parabola
. When the third parabola  is considered, the intersection point
is considered, the intersection point 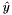 with the previously added parabola
with the previously added parabola 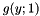 is found. Now two cases may arise:
is found. Now two cases may arise:
 , in which case all three parabolas belong to the envelope in the intervals
, in which case all three parabolas belong to the envelope in the intervals ![$ (-\infty,\bar y], (\bar y, \hat y], (\hat y, +\infty] $](form_120.png) .
.
 , in which case the second parabola
, in which case the second parabola 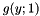 has no point beloning to the envelope, and it is removed. One then remains with the two parabolas
has no point beloning to the envelope, and it is removed. One then remains with the two parabolas 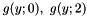 and the algorithm is re-iterated.
and the algorithm is re-iterated.
The algorithm proceeds in this fashion. Every time a new parabola is considered, its intersection point with the previously added parabola on the left is computed, and that parabola is potentially removed. The cost of an iteration is 1 plus the number of deleted parabolas. Since there are  iterations and at most
iterations and at most  parabolas to delete overall, the complexity is linear, i.e.
parabolas to delete overall, the complexity is linear, i.e.  .
.
| vl_image_distance_transform_f | ( | float const * | image, |
| vl_size | numColumns, | ||
| vl_size | numRows, | ||
| vl_size | columnStride, | ||
| vl_size | rowStride, | ||
| float * | distanceTransform, | ||
| vl_uindex * | indexes, | ||
| float | coeff, | ||
| float | offset | ||
| ) |
- See also:
- vl_image_distance_transform_d
| vl_imconvcol_vd | ( | double * | dst, |
| vl_size | dst_stride, | ||
| double const * | src, | ||
| vl_size | src_width, | ||
| vl_size | src_height, | ||
| vl_size | src_stride, | ||
| double const * | filt, | ||
| vl_index | filt_begin, | ||
| vl_index | filt_end, | ||
| int | step, | ||
| unsigned int | flags | ||
| ) |
Convolve image along columns.
- Parameters:
-
dst destination image. dst_stride width of the destination image including padding. src source image. src_width width of the source image. src_height height of the source image. src_stride width of the source image including padding. filt filter kernel. filt_begin coordinate of the first filter element. filt_end coordinate of the last filter element. step sub-sampling step. flags operation modes.
The function convolves the column of the image src by the filter filt and saves the result to the image dst. The size of dst must be equal to the size of src. Formally, this results in the calculation
![\[ \mathrm{dst} [x,y] = \sum_{p=y-\mathrm{filt\_end}}^{y-\mathrm{filt\_begin}} \mathrm{src}[x,y] \mathrm{filt}[y - p - \mathrm{filt\_begin}] \]](form_94.png)
The function subsamples the image along the columns according to the parameter step. Setting step to 1 (one) computes the elements ![$\mathrm{dst}[x,y]$](form_95.png) for all pairs (x,0), (x,1), (x,2) and so on. Setting step two 2 (two) computes only (x,0), (x,2) and so on (in this case the height of the destination image is
for all pairs (x,0), (x,1), (x,2) and so on. Setting step two 2 (two) computes only (x,0), (x,2) and so on (in this case the height of the destination image is floor(src_height/step)+1).
Calling twice the function can be used to compute 2-D separable convolutions. Use the flag VL_TRANSPOSE to transpose the result (in this case dst has transposed dimension as well).
The function allows the support of the filter to be any range. Usually the support is filt_end = -filt_begin.
The convolution operation may pick up values outside the image boundary. To cope with this edge cases, the function either pads the image by zero (VL_PAD_BY_ZERO) or with the values at the boundary (VL_PAD_BY_CONTINUITY).
| vl_imconvcol_vf | ( | float * | dst, |
| vl_size | dst_stride, | ||
| float const * | src, | ||
| vl_size | src_width, | ||
| vl_size | src_height, | ||
| vl_size | src_stride, | ||
| float const * | filt, | ||
| vl_index | filt_begin, | ||
| vl_index | filt_end, | ||
| int | step, | ||
| unsigned int | flags | ||
| ) |
- See also:
- vl_imconvcol_vd
| vl_imconvcoltri_d | ( | double * | dest, |
| vl_size | destStride, | ||
| double const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride, | ||
| vl_size | filterSize, | ||
| vl_size | step, | ||
| int unsigned | flags | ||
| ) |
Convolve an image along the columns with a triangular kernel.
- Parameters:
-
dest destination image. destStride destination image stride. image image to convolve. imageWidth width of the image. imageHeight height of the image. imageStride width of the image including padding. filterSize size of the triangular filter. step sub-sampling step. flags operation modes.
The function convolves the columns of the image image with the triangular kernel
![\[ k(t) = \frac{1}{\Delta^2} \max\{ \Delta - |t|, 0 \}, \quad t \in \mathbb{Z} \]](form_125.png)
The paramter  , equal to the function argument filterSize, controls the width of the kernel. Notice that the support of
, equal to the function argument filterSize, controls the width of the kernel. Notice that the support of  as a continuous function of
as a continuous function of 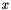 is the open interval
is the open interval  , which has length
, which has length  . However,
. However,  restricted to the ingeter domain
restricted to the ingeter domain  has support
has support 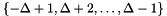 , which counts
, which counts 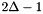 elements only. In particular, the discrete kernel is symmetric about the origin for all values of
elements only. In particular, the discrete kernel is symmetric about the origin for all values of  .
.
The normalization factor 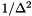 guaratnees that the filter is normalized to one, i.e.:
guaratnees that the filter is normalized to one, i.e.:
![\[ \sum_{t=-\infty}^{+\infty} k(t) = 1 \]](form_134.png)
- Algorithm
The function exploits the fact that convolution by a triangular kernel can be expressed as the repeated convolution by a rectangular kernel, and that the latter can be performed in time indepenedent on the fiter width by using an integral-image type trick. Overall, the algorithm complexity is independent on the parameter filterSize and linear in the nubmer of image pixels.
- See also:
- vl_imconvcol_vd for details on the meaning of the other parameters.
| vl_imconvcoltri_f | ( | float * | dest, |
| vl_size | destStride, | ||
| float const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride, | ||
| vl_size | filterSize, | ||
| vl_size | step, | ||
| int unsigned | flags | ||
| ) |
Convolve an image along the columns with a triangular kernel.
- See also:
- vl_imconvcoltri_d()
| VL_EXPORT void vl_imgradient_d | ( | double * | xGradient, |
| double * | yGradient, | ||
| vl_size | gradWidthStride, | ||
| vl_size | gradHeightStride, | ||
| double const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
| VL_EXPORT void vl_imgradient_f | ( | float * | xGradient, |
| float * | yGradient, | ||
| vl_size | gradWidthStride, | ||
| vl_size | gradHeightStride, | ||
| float const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
| vl_imgradient_polar_d | ( | double * | amplitudeGradient, |
| double * | angleGradient, | ||
| vl_size | gradWidthStride, | ||
| vl_size | gradHeightStride, | ||
| double const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
Compute gradient mangitudes and directions of an image.
- Parameters:
-
amplitudeGradient Pointer to amplitude gradient plane angleGradient Pointer to angle gradient plane gradWidthStride Width of the gradient plane including padding gradHeightStride Height of the gradient plane including padding image Pointer to the source image imageWidth Source image width imageHeight Source image height imageStride Width of the source image including padding.
This functions computes the amplitudes and angles of input image gradient.
Gradient is computed simple by gradient kernel 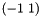 ,
, 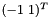 for border pixels and with sobel filter kernel
for border pixels and with sobel filter kernel 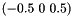 ,
,  otherwise on the input image image yielding x-gradient
otherwise on the input image image yielding x-gradient  , stored in xGradient and y-gradient
, stored in xGradient and y-gradient  , stored in yGradient, respectively.
, stored in yGradient, respectively.
The amplitude of the gradient, stored in plane amplitudeGradient, is then calculated as  and the angle of the gradient, stored in angleGradient is
and the angle of the gradient, stored in angleGradient is  normalised into interval 0 and
normalised into interval 0 and  .
.
This function also allows to process only part of the input image defining the imageStride as original image width and width as width of the sub-image.
Also it allows to easily align the output data by definition of the gradWidthStride and gradHeightStride .
| vl_imgradient_polar_f | ( | float * | amplitudeGradient, |
| float * | angleGradient, | ||
| vl_size | gradWidthStride, | ||
| vl_size | gradHeightStride, | ||
| float const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
- See also:
- vl_imgradient_polar_d
| VL_EXPORT void vl_imgradient_polar_f_callback | ( | float const * | sourceImage, |
| int | sourceImageWidth, | ||
| int | sourceImageHeight, | ||
| float * | dstImage, | ||
| int | dstWidth, | ||
| int | dstHeight, | ||
| int | octave, | ||
| int | level, | ||
| void * | params | ||
| ) |
| vl_imintegral_d | ( | double * | integral, |
| vl_size | integralStride, | ||
| double const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
Compute integral image.
- Parameters:
-
integral integral image. integralStride integral image stride. image source image. imageWidth source image width. imageHeight source image height. imageStride source image stride.
Let ![$ I(x,y), (x,y) \in [0, W-1] \times [0, H-1] $](form_144.png) . The function computes the integral image
. The function computes the integral image 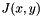 of
of  :
:
![\[ J(x,y) = \sum_{x'=0}^{x} \sum_{y'=0}^{y} I(x',y') \]](form_147.png)
The integral image 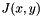 can be used to compute quickly the integral of of
can be used to compute quickly the integral of of  in a rectangular region
in a rectangular region ![$ R = [x',x'']\times[y',y''] $](form_149.png) :
:
![\[ \sum_{(x,y)\in[x',x'']\times[y',y'']} I(x,y) = (J(x'',y'') - J(x'-1, y'')) - (J(x'',y'-1) - J(x'-1,y'-1)). \]](form_150.png)
Note that the order of operations is important when the integral image has an unsigned data type (e.g. vl_uint32). The formula is easily derived as follows:
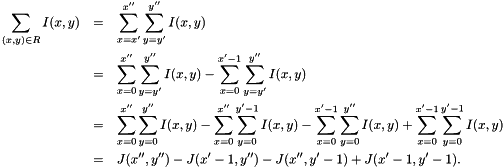
| vl_imintegral_f | ( | float * | integral, |
| vl_size | integralStride, | ||
| float const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
Compute integral image.
- See also:
- vl_imintegral_d.
| vl_imintegral_i32 | ( | vl_int32 * | integral, |
| vl_size | integralStride, | ||
| vl_int32 const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
Compute integral image.
- See also:
- vl_imintegral_d.
| vl_imintegral_ui32 | ( | vl_uint32 * | integral, |
| vl_size | integralStride, | ||
| vl_uint32 const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | imageWidth, | ||
| vl_size | imageHeight, | ||
| vl_size | imageStride | ||
| ) |
Compute integral image.
- See also:
- vl_imintegral_d.
| vl_imsmooth_d | ( | double * | smoothed, |
| vl_size | smoothedStride, | ||
| double const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | width, | ||
| vl_size | height, | ||
| vl_size | stride, | ||
| double | sigmax, | ||
| double | sigmay | ||
| ) |
Smooth an image with a Gaussian filter.
- Parameters:
-
smoothed smoothedStride image width height stride sigmax sigmay
| vl_imsmooth_f | ( | float * | smoothed, |
| vl_size | smoothedStride, | ||
| float const * | image, | ||
| vl_size | width, | ||
| vl_size | height, | ||
| vl_size | stride, | ||
| double | sigmax, | ||
| double | sigmay | ||
| ) |
Smooth an image with a Gaussian filter.
- See also:
- vl_imsmooth_d