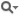00001
00002 """
00003 Description:
00004 Create a two-state state machine where one state writes to userdata and
00005 the other state reads from userdata, and spews a message to rosout.
00006
00007 Usage:
00008 $> ./user_data.py
00009
00010 Output:
00011 [INFO] : State machine starting in initial state 'SET' with userdata:
00012 []
00013 [INFO] : State machine transitioning 'SET':'set_it'-->'GET'
00014 [INFO] : >>> GOT DATA! x = True
00015 [INFO] : State machine terminating 'GET':'got_it':'succeeded'
00016 """
00017
00018 import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('asmach_tutorials')
00019 import rospy
00020 import asmach as smach
00021 import smach_ros
00022
00023 class Setter(smach.State):
00024 def __init__(self):
00025 smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes = ['set_it'], output_keys = ['x'])
00026 def execute(self, ud):
00027 ud.x = True
00028 return 'set_it'
00029
00030 class Getter(smach.State):
00031 def __init__(self):
00032 smach.State.__init__(self, outcomes = ['got_it'], input_keys = ['x'])
00033 def execute(self, ud):
00034 rospy.loginfo('>>> GOT DATA! x = '+str(ud.x))
00035 return 'got_it'
00036
00037 def main():
00038 rospy.init_node('smach_example_user_data')
00039
00040
00041 sm = smach.StateMachine(outcomes=['succeeded'])
00042
00043
00044 with sm:
00045
00046 smach.StateMachine.add('SET', Setter(), {'set_it':'GET'})
00047 smach.StateMachine.add('GET', Getter(), {'got_it':'succeeded'})
00048
00049
00050 outcome = sm.execute()
00051
00052 if __name__ == '__main__':
00053 main()